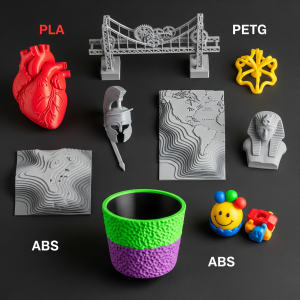
It’s a feeling every 3D printing enthusiast knows well. Hours into a print, you check on its progress, only to be greeted by a chaotic mess of plastic spaghetti, a detached object sliding around the build plate, or layers shifted so badly they resemble abstract art. The disappointment is real. The wasted filament stings.
Print failures happen to the best of us, from beginners to seasoned pros. But understanding why they happen is the key to drastically reducing them. Consider this your field guide to diagnosing and defeating those common gremlins that stand between you and printing perfection.
1. The First Layer Fiasco: When Things Don’t Stick (or Stick Too Much)
This is arguably the most critical part of any print. Get the first layer wrong, and the rest is doomed.
- The Problem: Prints detaching mid-print, warping at the corners, or an “elephant’s foot” where the base spreads out too wide.
- Common Culprits:
- Bed Leveling: The #1 suspect. An uneven bed or incorrect Z-offset (nozzle distance from the bed) is disastrous. Too far, and filament won’t adhere; too close, and it gets squished or blocks the nozzle.
- Bed Temperature: Too cool, and materials like PLA or PETG won’t stick well. Too hot can sometimes cause warping or elephant’s foot, especially with PLA.
- Dirty Build Surface: Fingerprints, dust, or old adhesive residue prevent proper adhesion.
- Field Fixes:
- Master Bed Leveling: Learn your printer’s procedure (manual or auto) and do it regularly! Print first-layer calibration tests.
- Clean Your Bed: Wipe down with Isopropyl Alcohol (IPA) before prints. Use glue stick or specialised adhesives if needed for certain materials/surfaces.
- Tune First Layer Settings: Use your slicer to print the first layer hotter and slower for better adhesion.
2. Stringing & Oozing: The Cobweb Catastrophe
Fine (or sometimes thick) strings of plastic spanning gaps in your print? That’s stringing or oozing.
- The Problem: Unsightly webs between separate parts of a model, requiring extensive cleanup.
- Common Culprits:
- Retraction Settings: Incorrect distance or speed when the filament is pulled back during travel moves.
- Print Temperature: Too hot, and the filament becomes overly liquid and oozes easily.
- Moisture in Filament: Wet filament turns water into steam when heated, causing popping and exacerbating oozing/stringing.
- Field Fixes:
- Calibrate Retraction: Print retraction test models to dial in the perfect distance and speed for your filament and printer setup.
- Print a Temp Tower: Find the lowest effective printing temperature for your filament that still provides good layer adhesion.
- Keep Filament Dry: Store filament in airtight containers with desiccant, especially materials like PETG and TPU. Consider a filament dryer if you live in a humid area (like coastal NSW).
3. Layer Shifting & Imperfections: When Things Go Sideways
Suddenly, your print’s layers are offset, or you see random blobs, zits, or inconsistent walls.
- The Problem: Visually jarring shifts or surface defects ruin the print’s geometry and appearance.
- Common Culprits:
- Mechanical Issues: Loose belts (X or Y axis), binding Z-axis rods, loose grub screws on motor pulleys.
- Printing Too Fast: Especially jerky movements (infill, travel) can cause the printer to lose steps if pushed beyond its limits.
- Inconsistent Extrusion: Partial nozzle clogs, or variations in filament diameter.
- Field Fixes:
- Mechanical Check-up: Regularly check belt tension and ensure all screws/pulleys are tight. Lubricate Z-axis rods if needed.
- Moderate Print Speeds: Especially outer walls and complex sections.
- Address Extrusion: Check for clogs (“cold pull” method). This leads us to a crucial, often overlooked factor…
4. The Unsung Variable: Filament Quality & Consistency
You can have a perfectly tuned printer and flawless slicer settings, but if your filament is inconsistent, you’ll still chase failures.
- The Problem: Underextrusion (gaps), overextrusion (blobs), brittleness causing snapping mid-print, poor layer adhesion, or even nozzle clogs – all can stem from subpar filament.
- Why Consistency Matters:
- Diameter Tolerance: Filament diameter varying even slightly throws off how much plastic your printer extrudes. High-quality filament maintains a consistent diameter (e.g., 1.75mm +/- 0.02mm).
- Material Purity & Additives: Consistent mixing ensures predictable printing temperatures and properties.
- Winding: A neatly wound spool prevents tangles that can stop a print dead.
- Dryness: Filament should be dry from the factory and properly sealed.
- The Reliable Foundation: Using filament you can trust removes a massive variable from the troubleshooting equation. When you know your filament behaves predictably, diagnosing mechanical or slicer issues becomes far easier.
Your Local Source for Reliable Prints
That’s why at N.E. 3D Printing, we’re meticulous about the filament we stock. We source high-quality filament, known for its tight tolerances, excellent consistency, and vibrant colours – designed to give you predictable, reliable results print after print.
And because we’re based right here in NSW, holding stock locally, you don’t have to wait weeks for that reliable foundation to arrive. When you’re battling print failures or just need a trustworthy spool for your next big project, we can get it to you quickly within Australia.
Ready to spend less time troubleshooting and more time creating?
Eliminate one major variable in your quest for perfect prints.
Check out our range of consistent, locally stocked filament:
Happy (and successful) printing!